Koo, Terry K, and Mae Y Li. “A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research.” Journal of chiropractic medicine vol. 15,2 (2016): 155-63. doi:10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012
Taha, Abdel Aziz, and Allan Hanbury. “Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: analysis, selection, and tool.” BMC medical imaging vol. 15 29. 12 Aug. 2015, doi:10.1186/s12880-015-0068-x
wikipedia
김장우, and 김종효. "3 차원 의료 영상 분할 평가 지표에 관한 고찰." 대한의학영상정보학회지 23.1 (2017): 14-20.
자동 영상 분할 결과의 유사도를 정량적으로 표현할 때, Dice similarity coefficient를 많이 사용함.
Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC)는 대표적인 overlap 기반 평가 지표
Intraclass Correlation Coefficients (ICC)는 대표적인 확률 기반 평가 지표
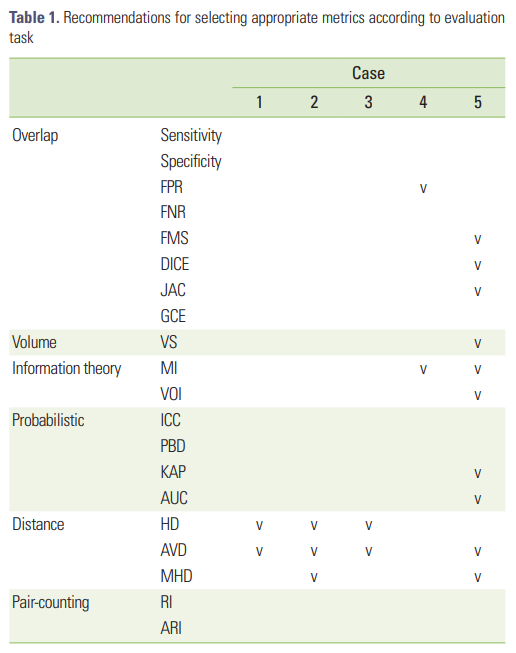
각 케이스에 적용할 수 있는 metrics는 다음 테이블 참조(링크)
Difference between DSC and ICC
- Dice Similarity Coefficient is a measure of how much 2 segmentations overlap in volume. The higher DSC, the better correspondence in volume between 2 raters.
- ICC measures a correlation between two independent approaches on a series of data
Dice Similarity Coefficient
• DSC = 2|X ⋂ Y| / ( |X| + |Y| )
X, Y = Given sets
|X| = cardinalities (집합의 크기) of the set X
|Y| = cardinalities (집합의 크기) of the set Y
• DSC = 2TP / (2TP+FP+FN)
댓글
댓글 쓰기